Application notes
Technical notes
Ask an engineer
Publications
United States (EN)
Select your region or country.
MEMS Mirrors Questions & Answers
- What type of MEMS mirror does Hamamatsu make?
- What are the advantages of electromagnetic mirrors?
- What is the relationship between mechanical deflection angle and optical deflection angle?
- Can you sell MEMS mirrors in chip form?
- What is the relationship between resolution and frame rate?
- What is a MEMS mirror?
- How are resonant and linear mirrors different?
- Why do you need a feedback loop for the resonant axis frequency?
What type of MEMS mirror does Hamamatsu make?
Hamamatsu makes electromagnetic mirrors, which consist of a magnet and a MEMS mirror chip. The basic operating principle of electromagnetic mirrors is shown in the figure below. When an electrical current flows into the coil on the MEMS mirror, the mirror tilts according to the Lorentz force.
See MEMS mirrors on our main website
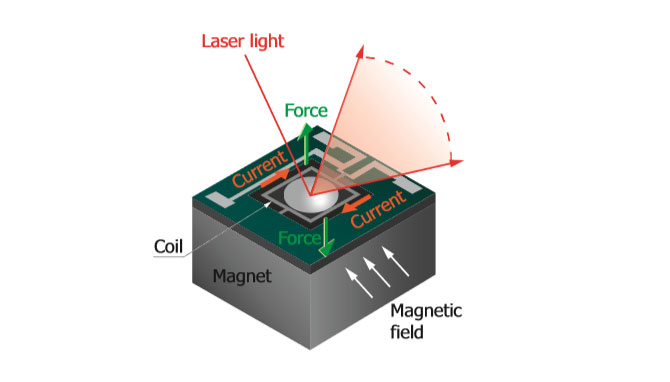
Figure 1. An electromagnetic mirror’s structure and basic operating principle
What are the advantages of electromagnetic mirrors?
The advantages of electromagnetic mirrors include the following:
- Low voltage operation (up to 12 V)
- Large torque
- Large tilt angle
What is the relationship between mechanical deflection angle and optical deflection angle?
As shown in the figure below, the mechanical deflection angle and optical deflection angle have the following relationship:
Optical deflection angle = 2 x Mechanical deflection angle
Hamamatsu uses the optical deflection angle in our datasheets.
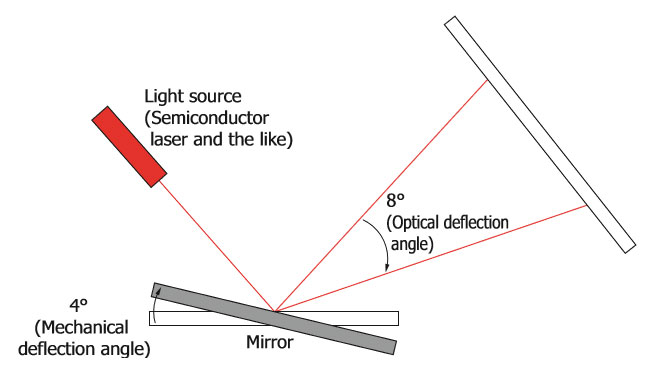
Figure 2. Optical deflection angle
Can you sell MEMS mirrors in chip form?
We do not sell MEMS mirrors in chip form. The MEMS mirror packaging and assembly are very critical factors for obtaining the performance described in the datasheet. Therefore, we cannot sell these components separately.
What is the relationship between resolution and frame rate?
In raster scanning, there is a trade-off between vertical resolution and frame rate. The horizontal scanning time is determined by the resonant frequency of the fast axis (fixed frequency). When you increase the horizontal resolution, the time to scan a whole frame also increases. Therefore, it results in a slower frame rate. Typical vertical resolution and frame rate values are shown in the table below.
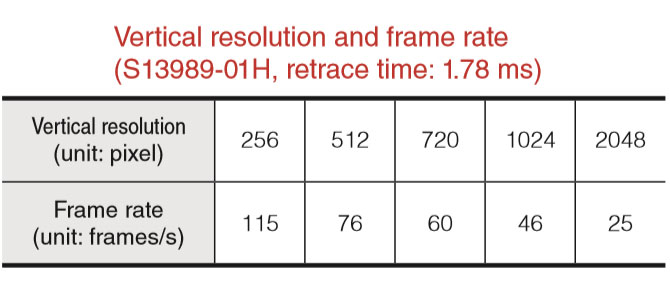
Table 1. Vertical resolution and frame rate values
What is a MEMS mirror?
MEMS stands for micro-electro-mechanical systems, and a MEMS mirror is a small moving mirror etched on a silicon wafer using MEMS technology. By using a MEMS mirror, you can reduce the size of the whole scanner to a few cm cube.
How are resonant and linear mirrors different?
A resonant mirror moves in a continuous sinusoidal motion at the fixed frequency, usually 1 kHz to tens of kHz. You can get a wide mirror angle with a small driving electric current. For example, our S13989-01H resonant mirror is capable of +/-20 deg. optical angles with +/-25 mA driving current.
A linear mirror tilts its angle according to the driving current. You can stop the mirror at the desired angle or operate it in continuous movement. However, in continuous mode the speed is usually limited to tens of Hz.
Why do you need a feedback loop for the resonant axis frequency?
The mirror’s tilt angle is significantly affected by even a slight shift in the resonant frequency. The resonant frequency can shift over time and when the temperature changes. The feedback loop adjusts the mirror driver frequency to match the shifted resonant frequency, so it can minimize the tilt angle instability.
If you have a technical question you’d like to see answered on this page, email us.
Meet the engineer

Mario is a MEMS mirror applications engineer. A music enthusiast, his keen interest in audio systems and electric guitar drew him to electrical engineering. Sound analysis of shamisen, a Japanese musical instrument, was the focus of his graduate studies. Mario still enjoys music-related hobbies such as building audio speakers, playing the jazz guitar, and salsa dancing.
- Confirmation
-
It looks like you're in the . If this is not your location, please select the correct region or country below.
You're headed to Hamamatsu Photonics website for US (English). If you want to view an other country's site, the optimized information will be provided by selecting options below.
In order to use this website comfortably, we use cookies. For cookie details please see our cookie policy.
- Cookie Policy
-
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in this cookie policy. By closing the cookie warning banner, scrolling the page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
Hamamatsu uses cookies in order to enhance your experience on our website and ensure that our website functions.
You can visit this page at any time to learn more about cookies, get the most up to date information on how we use cookies and manage your cookie settings. We will not use cookies for any purpose other than the ones stated, but please note that we reserve the right to update our cookies.
1. What are cookies?
For modern websites to work according to visitor’s expectations, they need to collect certain basic information about visitors. To do this, a site will create small text files which are placed on visitor’s devices (computer or mobile) - these files are known as cookies when you access a website. Cookies are used in order to make websites function and work efficiently. Cookies are uniquely assigned to each visitor and can only be read by a web server in the domain that issued the cookie to the visitor. Cookies cannot be used to run programs or deliver viruses to a visitor’s device.
Cookies do various jobs which make the visitor’s experience of the internet much smoother and more interactive. For instance, cookies are used to remember the visitor’s preferences on sites they visit often, to remember language preference and to help navigate between pages more efficiently. Much, though not all, of the data collected is anonymous, though some of it is designed to detect browsing patterns and approximate geographical location to improve the visitor experience.
Certain type of cookies may require the data subject’s consent before storing them on the computer.
2. What are the different types of cookies?
This website uses two types of cookies:
- First party cookies. For our website, the first party cookies are controlled and maintained by Hamamatsu. No other parties have access to these cookies.
- Third party cookies. These cookies are implemented by organizations outside Hamamatsu. We do not have access to the data in these cookies, but we use these cookies to improve the overall website experience.
3. How do we use cookies?
This website uses cookies for following purposes:
- Certain cookies are necessary for our website to function. These are strictly necessary cookies and are required to enable website access, support navigation or provide relevant content. These cookies direct you to the correct region or country, and support security and ecommerce. Strictly necessary cookies also enforce your privacy preferences. Without these strictly necessary cookies, much of our website will not function.
- Analytics cookies are used to track website usage. This data enables us to improve our website usability, performance and website administration. In our analytics cookies, we do not store any personal identifying information.
- Functionality cookies. These are used to recognize you when you return to our website. This enables us to personalize our content for you, greet you by name and remember your preferences (for example, your choice of language or region).
- These cookies record your visit to our website, the pages you have visited and the links you have followed. We will use this information to make our website and the advertising displayed on it more relevant to your interests. We may also share this information with third parties for this purpose.
Cookies help us help you. Through the use of cookies, we learn what is important to our visitors and we develop and enhance website content and functionality to support your experience. Much of our website can be accessed if cookies are disabled, however certain website functions may not work. And, we believe your current and future visits will be enhanced if cookies are enabled.
4. Which cookies do we use?
There are two ways to manage cookie preferences.
- You can set your cookie preferences on your device or in your browser.
- You can set your cookie preferences at the website level.
If you don’t want to receive cookies, you can modify your browser so that it notifies you when cookies are sent to it or you can refuse cookies altogether. You can also delete cookies that have already been set.
If you wish to restrict or block web browser cookies which are set on your device then you can do this through your browser settings; the Help function within your browser should tell you how. Alternatively, you may wish to visit www.aboutcookies.org, which contains comprehensive information on how to do this on a wide variety of desktop browsers.
5. What are Internet tags and how do we use them with cookies?
Occasionally, we may use internet tags (also known as action tags, single-pixel GIFs, clear GIFs, invisible GIFs and 1-by-1 GIFs) at this site and may deploy these tags/cookies through a third-party advertising partner or a web analytical service partner which may be located and store the respective information (including your IP-address) in a foreign country. These tags/cookies are placed on both online advertisements that bring users to this site and on different pages of this site. We use this technology to measure the visitors' responses to our sites and the effectiveness of our advertising campaigns (including how many times a page is opened and which information is consulted) as well as to evaluate your use of this website. The third-party partner or the web analytical service partner may be able to collect data about visitors to our and other sites because of these internet tags/cookies, may compose reports regarding the website’s activity for us and may provide further services which are related to the use of the website and the internet. They may provide such information to other parties if there is a legal requirement that they do so, or if they hire the other parties to process information on their behalf.
If you would like more information about web tags and cookies associated with on-line advertising or to opt-out of third-party collection of this information, please visit the Network Advertising Initiative website http://www.networkadvertising.org.
6. Analytics and Advertisement Cookies
We use third-party cookies (such as Google Analytics) to track visitors on our website, to get reports about how visitors use the website and to inform, optimize and serve ads based on someone's past visits to our website.
You may opt-out of Google Analytics cookies by the websites provided by Google:
https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout?hl=en
As provided in this Privacy Policy (Article 5), you can learn more about opt-out cookies by the website provided by Network Advertising Initiative:
http://www.networkadvertising.org
We inform you that in such case you will not be able to wholly use all functions of our website.
Close